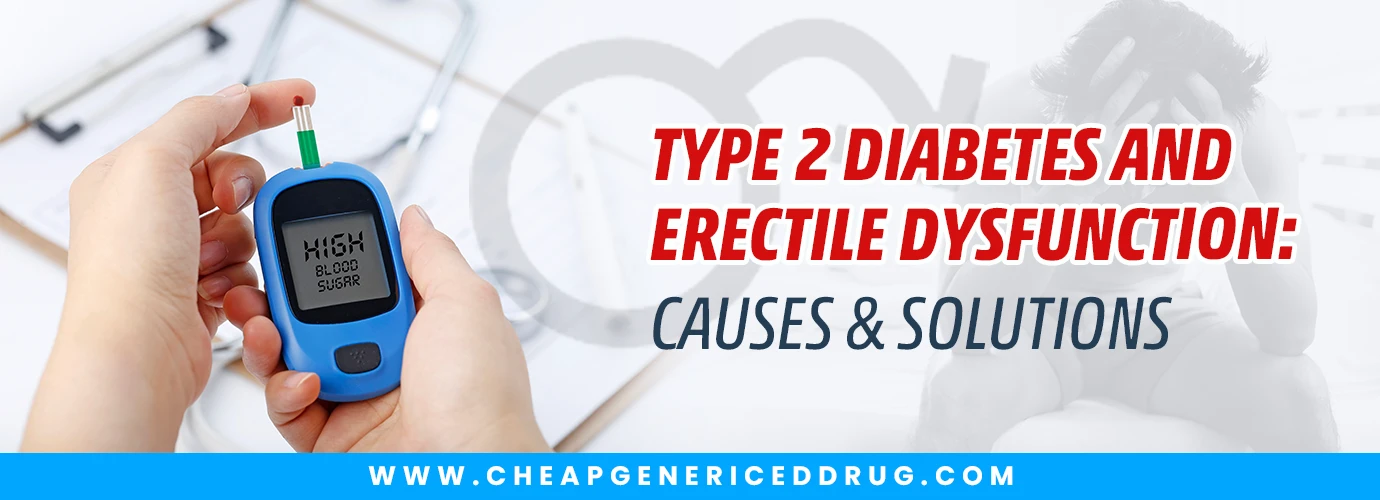
Living with type 2 diabetes affects more than blood sugar—it can also impact sexual health. One of the most common complications is erectile dysfunction (ED). Men with diabetes type 2 and erectile dysfunction often feel frustrated, but knowing the connection can make treatment easier. This blog explains how erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes are linked, the best type 2 diabetes and erectile dysfunction treatment options, and how lifestyle changes can help.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Before diving into sexual health, let’s review the basics. What is type 2 diabetes? It is a condition where your body cannot use insulin properly, leading to high blood sugar. Over time, this damages blood vessels, nerves, and vital organs.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common form, usually diagnosed in adults, though cases in young people are rising.
- It is different from type 1 diabetes vs type 2—in type 1, the body makes no insulin at all, while in diabetes type 2, insulin is produced but used poorly.
- Knowing the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes helps in understanding treatment approaches.
Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Recognizing type 2 diabetes symptoms early helps prevent complications, including ED. Common signs of type 2 diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Extreme thirst
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
These are also called symptoms of diabetes type 2. If ignored, they may lead to severe issues like erectile dysfunction and diabetes type 2 complications.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
The exact causes vary, but the main risk factors include:
- Genetics (yes, is type 2 diabetes genetic? – heredity increases risk)
- Obesity and lack of exercise
- Poor diet high in refined sugar and fats
- Age over 40 (though it now appears earlier)
When blood sugar stays high, it damages blood vessels and nerves, which explains why it often go hand in hand.
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes: The Differences
The type 2 diabetes vs type 1 comparison is important:
- Type 1 diabetes vs type 2 → Type 1 is autoimmune; Type 2 is lifestyle and genetic.
- Diabetes type 1 vs type 2 → Type 1 requires lifelong insulin; Type 2 can sometimes be controlled with lifestyle and type 2 diabetes medications.
- Type 1 and type 2 diabetes → Both cause high blood sugar, but treatments differ.
Understanding the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes also highlights why ED is more common in Type 2.
How Type 2 Diabetes Causes Erectile Dysfunction?
The link between type 2 diabetes and erectile dysfunction is clear:
- Nerve damage – High blood sugar damages penile nerves.
- Poor blood circulation – Arteries narrow, limiting blood flow needed for erections.
- Hormonal imbalance – Low testosterone is common in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Psychological stress – Diabetes leads to anxiety, which worsens ED.
Thus, erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes become interconnected issues.
Type 2 Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction Treatment
Managing both conditions requires a mix of self-care, medication, and sometimes medical devices. Effective treatment includes:
- Blood sugar control (prevent further damage)
- Oral ED medications like sildenafil or tadalafil
- Hormone therapy if testosterone is low
- Lifestyle changes such as exercise and quitting smoking
- Devices or surgery for severe cases
The sooner you manage diabetes, the better your chances of reversing erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Health
Lifestyle is central in type 2 diabetes self-care and preventing ED. Simple changes include:
- Following a proper type 2 diabetes diet with lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Using a type 2 diabetes food list to avoid high-sugar foods.
- Regular exercise to improve circulation and reduce stress.
- Stopping smoking and limiting alcohol.
Healthy choices reduce both symptoms of type 2 diabetes and ED.
Medications for Type 2 Diabetes and ED
For men managing diabetes type 2, medications play a key role. Common type 2 diabetes medications include:
- Metformin – lowers glucose production
- Sulfonylureas – increase insulin release
- DPP-4 inhibitors & GLP-1 agonists – improve insulin response
- Insulin therapy – for advanced stages
Alongside these, ED drugs can improve erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes symptoms.
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Reversed?
One of the most common questions is: Can you reverse type 2 diabetes?
- With weight loss, healthy eating, and exercise, many people achieve remission.
- So, is type 2 diabetes reversible? In some cases, yes—especially when caught early.
- However, if severe nerve or blood vessel damage has occurred, ED may remain even after sugar levels improve.
Thus, early management is vital to prevent diabetes type 2 and erectile dysfunction.
Blood Sugar Danger Levels and ED
Men often ask: What level of blood sugar is dangerous for type 2 diabetes?
- A fasting blood sugar consistently above 126 mg/dL or an A1C above 6.5% is considered diabetic.
- Higher, uncontrolled levels accelerate ED risk by damaging penile blood vessels.
This is why regular monitoring is a crucial part of type 2 diabetes treatment and sexual health care.
Medical and Surgical Treatments
When lifestyle and medications fail, other treatments help:
- Vacuum devices to draw blood into the penis
- Penile injections or suppositories (alprostadil)
- Surgical implants for severe, long-term cases
These options show how the treatment can be customized for every man.
Type 2 Diabetes Self-Care Checklist
Here’s a quick self-care guide:
- Monitor glucose daily
- Follow a type 2 diabetes diet
- Take prescribed type 2 diabetes medication on time
- Exercise regularly
- Manage stress
- Attend checkups for complications
This improves not only overall health but also reduces the risk of erectile dysfunction and diabetes type 2 problems.
ICD-10 and Clinical Notes
For medical classification, type 2 diabetes ICD 10 is E11. This code is used in clinical records for type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications, including ED.
Final Thoughts
The relationship between these is strong, but not hopeless. With proper care, many men manage both conditions successfully.
- Understand the symptoms of diabetes type 2 and treat them early.
- Focus on type 2 diabetes treatments, including diet, exercise, and medication.
- Use medical help when needed for erectile dysfunction and type 2 diabetes.
By combining self-care with medical support, men can improve their health, regain confidence, and enjoy better quality of life.